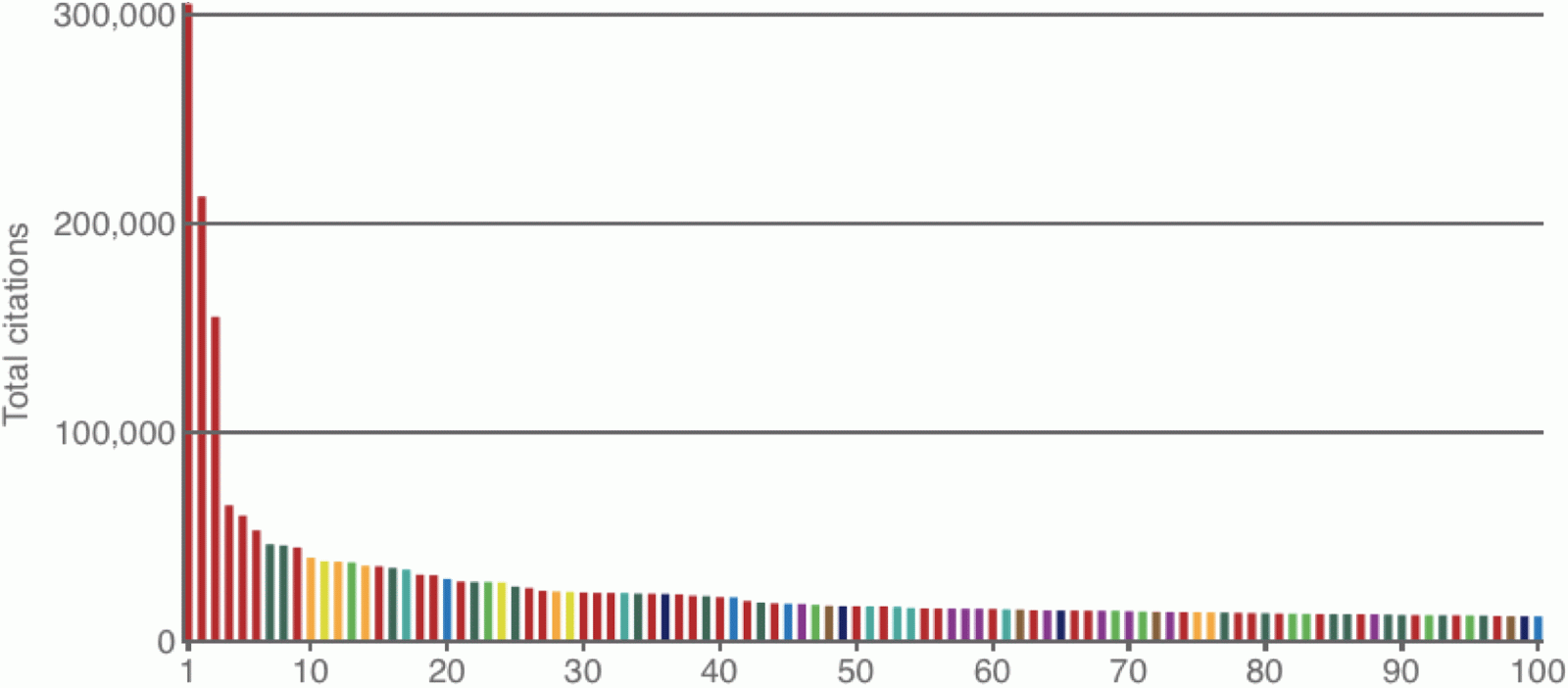
For those of you who have missed it, the magazine Nature has recently looked at the 100 most highly cited science papers of all time (across all fields):
van Noorden R, Maher B, Nuzzo R (2014) The top 100 papers: Nature explores the most-cited research of all time. Nature 514: 550-553.The list is dominated by biology papers, with biochemical laboratory techniques taking all of the top spots. However, it also worth noting that bioinformatics papers produce a very good showing, and so I have extracted 10 of them here.
If you have ever wondered what phylogenetic tree-building method is most used then it is at #20, while the most-used tree-building program is at #45 (having got there in only 7 years). You may also wonder why sequence alignment programs (#10 & #28 for Clustal; #12 & #14 for BLAST) do much better than tree-building programs (#45 for MEGA; #75 for GCG; #100 for MrBayes).
As for journals, the papers appeared in Nucleic Acids Research (4), Molecular Biology & Evolution (2), Bioinformatics (2), Journal of Molecular Biology (1) and Evolution (1). This list only partially matches their Journal Citation Reports current 5-Year Impact Factors: 8.378, 10.494, 6.968, 3.795 and 5.469, respectively.
Rank: 10 Citations: 40,289
Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice.
Thompson, J. D., Higgins, D. G. & Gibson, T. J
Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 4673–4680 (1994).
Rank: 12 Citations: 38,380
Basic local alignment search tool.
Altschul, S. F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E. W. & Lipman, D. J.
J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403–410 (1990).
Rank: 14 Citations: 36,410
Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs.
Altschul, S. F. et al.
Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 3389–3402 (1997).
Rank: 20 Citations: 30,176
The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees.
Saitou, N. & Nei, M.
Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425 (1987).
Rank: 28 Citations: 24,098
The CLUSTAL_X Windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools.
Thompson, J. D., Gibson, T. J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F. & Higgins, D. G.
Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 4876–4882 (1997).
Rank: 41 Citations: 21,373
Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap.
Felsenstein, J.
Evolution 39, 783–791 (1985).
Rank: 45 Citations: 18,286
MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M. & Kumar, S.
Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 1596–1599 (2007).
Rank: 75 Citations: 14,226
A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX.
Devereux, J., Haeberli, P. & Smithies, O.
Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 387–395 (1984).
Rank: 76 Citations: 14,099
MODELTEST: Testing the model of DNA substitution.
Posada, D. & Crandall, K. A.
Bioinformatics 14, 817–818 (1998).
Rank: 100 Citations: 12,209
MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models.
Ronquist, F. & Huelsenbeck, J. P.
Bioinformatics 19, 1572–1574 (2003).

No comments:
Post a Comment